Vitamin C Cancer Treatments
INDEX
1.
New development: Oral Liposomal Vitamin C:
(L-AA) = > Cancer-killing AA blood concentration.
2.
Recent Studies 2009, ‘12, ‘13 IV AA: Riordan,
Japanese Meta Study, etc.
3.
Vitamin C in Cancer Treatment Cameron & Pauling Report #14
4.
Overview of Vitamin C and Cancer as of 2000
Linus Pauling Institute summary of papers.
5.
Dr Frederick Klenner, vitamin C history
and treatments overview
6.
Dr Klenner writes in 1971: Could ascorbic acid
have anti-cancer features?
7.
Dr Lendon H Smith: Clinical Guide to Klenner's
Use of Vitamin C
8.
Klenner’s Comments: AA utilization by
the body in malignancy
9. Klenner’s Cancer Protocol
11.
Dr Klenner summarized his cancer paper
12.
Klenner’s tests during treatment
13.
From Klenner’s Case Histories
14.
Sugar & diabetes, increase immune
system tumor tolerance
15.
From Linus Pauling Institute (LPI) at
Oregon State University
16.
Digression from LPI to present successful clinical results
17.
Necessary Treatment Dosage Criteria
19.
Back to LPI material LPI Clinical Trials
20.
Matthias Rath, was a Pauling associate: Quote: “Cancer tumor growth can be stopped”
21.
Ketosis helps; Glycemia hinders effective treatment
22.
Serrapeptase
Enzyme (SpE) Attacks Tumor Sheath
23.
Rome Cancer Clinic treats Cancer as a Fungal/Yeast
24.
Gerson’s Diet that cures cancer:
25. FDA Ban
on pre-formulated AA injections
26.
AA/SA Antioxidant/Oxidant mechanisms
29.
Vitamin C, Infectious Diseases, and Toxins: Curing
the Incurable
30.
References: Most relevant Vitamin C tribal
knowledge
31.
John Ely References on Nutrition, AA, CoQ10, and
Life Extension
32.
AA Headlines:
33.
References Vitamin C vs. Hyaluronate Lyase
Enzyme
Vitamin C Cancer Treatments
New Development: It is now time for the miss-information and stonewalling of vitamin C to end.
Oral Liposomal AA (L-AA)
has significantly higher blood adsorption and 98% vs. the ~20% transfer
effectiveness for plain AA powder. L-AA
has ~5 times the transport effectiveness that was achievable before. The gut to blood transfer no longer has a
practical upper limit because the loose bowel phenomenon does not happen when
AA is surrounded by Lecithin, a lipid emulsifier. The Lecithin also facilitates the transport of the AA to lipid
membrane microbes where it can be oxidized and the dehydroxy ascorbic acid
(DHA) produced can be readily ingested by the microbes in place of sugars they
crave. The ingested DHA kills
sugar-eating microbes and cancer cells. But the AA level must be high enough.
Now it can be.
Optional microbe killing lipids like vitamins [A, E,
& D], EGCG,
coconut oil, capric & caprylic acids [anti-yeast], palmitic acid [butter],
and olive oil can be included in the Lecithin lipid mix. Xylitol (a healthful sugar
alcohol) that has anti-bacterial and anti-yeast properties can be used as a
sweetener.
The levels of blood AA concentration that was
historically found effective (by Klenner, Cathcart, and others) against
bacteria and viruses in the blood was achievable only with continuous sodium
ascorbate IV supplemented with oral AA. The sessions could take several days to
weeks and were both inconvenient and expensive. Only a few doctors provided these services. Many doctors remained skeptical of their
value because of flawed AA effectiveness studies. These treatment modalities were a real bother.
We can now produce consistently high blood AA by
intake of several grams of oral L-AA every hour during waking hours for a
period of days in an outpatient mode of treatment. The presence of the doctor is no longer necessary, just like it
is not needed for most prescribed drugs.
L-AA is anti inflammatory by its nature; at high
enough dosages it acts like an antibiotic plus antiviral plus anticancer chemo
drug, with very few side effects. The
history of this AA treatment is described below. What is new is the high blood active AA levels can be achieved by
oral intake alone. To further improve this AA treatment, ketosis (See Atkins
low carb diet induction) should be invoked. Xylitol
should be used in place of sugar to force sugar using bacteria and yeasts to
die back and gene shift to using Xylitol in place of sugar. The gene shift
greatly reduces the pathogenicity of the microbes and yeasts. See our AA Ketonic
Protocol discussion. A video
shows how to make your
own L-AA.
INTRODUCTION
Vitamin C is also called Ascorbic Acid (AA). Another (IV) form is Sodium Ascorbate (SA). This collection of notes on cancer treatment is mostly based on Vitamin C, not as a vitamin, but as the primary active medicine.
However,
other elements and protocol factors can be used in a combined protocol. See AA Ketonic Protocols for the
mathematical theory of multi factored protocols. Some of the other factors are pointed to near the end of the notes.
When
vitamin C is used as a medicine its pharmacokinetics
and pharmacodynamics need to be considered and followed. Its use as an
antioxidant means it switches from active (reducing) form to oxidizing form
instantly when the molecule interacts with an oxide molecule. Thus the active form concentration in the
blood changes rapidly when ROS/NOS are present and the patient is in the scurvy
state. For this reason high amounts of
AA need to be supplied depending on the amounts of toxins or oxides that are
present. The sicker the patient is, the
more AA needs to be supplied and will be consumed rapidly. The patient’s hunger
for AA expresses itself as allergies, pain, inflammation, redness, itching and
feelings of sickness.
Much of the material here is derived from writings by Ewan Cameron, Linus Pauling, Frederick Klenner, Cathcart, John Ely, Andriew Saul, Lendon Smith. Many of their papers are hot linked directly in the notes with only a brief summary. There is much practical wisdom to be found in these papers, which should be read carefully to understand how vitamin C works as a medical molecule to kill cancer cells.
Holisticcancersolutions.com
Report #14 Vitamin C in Cancer Treatment
“30 years ago [1979] Dr. Pauling co-authored a book
with Ewan Cameron MD, titled, Cancer and Vitamin C: A Discussion
of the Nature, Causes, Prevention, and Treatment of Cancer With Special
Reference to the Value of Vitamin C. The book is
available at Amazon. . It may be of special interest to cancer patients what
some of the readers recently wrote about the book:
”Cameron and Pauling prove with clinical studies
that large doses of Vitamin C taken over long periods of time are effective in
controlling many cancers. Linus Pauling earned two Nobel Prizes. He deserved a
third Nobel for this book.” Book
Finder
Recent
Studies 2009, ‘12, ‘13 Some IV
Treatment Successes and Some Insensitivities.
Riordan Clinic
Research Overview Cancer, IV Ascorbic Acid, Nutrients, and videos.
Riordan
IV AA vs Cancer Clinical Statistics Statistical
summary of clinical histories of IV AA therapy and results. Spans 30 years and
over 300 cancer patients, animal cancer research, and IV AA treatments.
Riordan
Orthomolecular Research Journal Archive
Many
articles showing treatments and results.
High-dose Vitamin C (Ascorbic
Acid) Therapy in the Treatment of Patients with Advanced Cancer S.
Ohno, et al; Journal of
International Cancer Research and Treatment
A comprehensive overview of IV and other treatment methods, mechanisms and history. More of a Meta-Study, with limited inputs.
From the Abstract:
“….As research results concerning ascorbate pharmacokinetics and its mechanisms of action against tumor cells have been published, and as evidence from case studies has continued to mount that ascorbate therapy could be effective if the right protocols were used, interest among physicians and scientists has increased. In this review, high-dose vitamin C therapy in cancer treatment is re-evaluated.”
Clinical Studies:
“Recently, Padayatty et al. reported well-documented cases of advanced carcinomas in accordance with NCI Best Case Series guidelines (56). In all three cases, high-dose intravenous vitamin C therapy effectively reduced the progression of a malignant tumor and improved the health status of these patients. Unfortunately, information on the plasma vitamin C concentrations of these patients is not available to establish a causal relationship between the route of administration, the resultant effective concentrations, and the observedVol 10 therapeutic effect. However, in the light of recent clinical pharmacokinetic findings and in vitro evidence of antitumor mechanisms, these case reports indicate that the role of high-dose intravenous vitamin C therapy in cancer treatment should be reassessed.”
The conclusion is equivocal but it calls for removal
of blocks on funding for Ascorbate Research.
More recent studies 2012 and 2013
Effect of
high-dose intravenous vitamin C on inflammation in cancer patients N. Mikirova, et al. Journal
of Translational Medicine, Vol 10,
2012
The Effects of High
Concentrations of Vitamin C on Cancer Cells --Seyeon Park, 2013
“Of the nine patients with
the in vitro assay indicating their leukemic cells were sensitive to vitamin C,
seven exhibited a clinical response, compared with none of the six patients who
were insensitive to vitamin C.”
Overview of Vitamin C and
Cancer as of 2000
Linus Pauling Institute summary of many prior
papers.
“What can we conclude about vitamin C and cancer? While the theoretical speculation by Dr. Golde seems plausible, there is no clinical evidence that supplemental antioxidant vitamins, including vitamin C, harm cancer patients. Indeed, much of the recent cell culture and clinical research suggests that a combination of antioxidant vitamins and minerals as an adjunct to conventional therapy may have benefit. This is a complex issue, however, and there is clearly more to learn from controlled clinical trials about the use of these modalities in treating cancer before definitive conclusions can be drawn.”
Recent Publications of the
LPI
Dr Frederick Klenner,
vitamin C history and treatments overview.
Dr Klenner treated about 3000 patients with AA. Dr Cathcart treated over 4000 with AA.
Dr Klenner writes in 1971: Could ascorbic acid have
anti-cancer features?
“Schlegel[50] from Tulane University has been using 1.5 grams ascorbic acid daily to prevent recurrences of cancer of the bladder. He and biochemist Pipkin have been able to demonstrate that in the presence of ascorbic acid, carcinogenic metabolites will not develop in the urine. They suggest that spontaneous tumor formation is the result of faulty tryptophan metabolism while urine is retained in the bladder. Schlegel termed ascorbic acid "An Anticancer Vitamin". Along this line Glick and Hosoda[51] reported on work by Von Numers and Pettersson that the depletion of mast cells from guinea pigs skin was due to ascorbic acid deficiency. The possibilities indicated are that vitamin C is necessary either directly or indirectly for formation of mast cells, or for their maintenance once formed or both. Ascorbic acid will control myelocytic leukemia provided 25 to 30 grams are taken orally each day.
“One
can only speculate on what massive therapy would do in all forms of cancer.
Many pathologic conditions are cured by giving 5 million to 100,000 million
units of penicillin as an intravenous drip over a period of 4 to 6 weeks. How
long must we wait for someone to start continuous ascorbic acid drip for 2 to 3
months, giving 100 to 300 grams each day, for various malignant conditions?”
Dr
Lendon H Smith: (LHS) Clinical Guide to Klenner's Use of Vitamin C 1988.htm
LHS--“For a very severe illness, the dose he used was large and the most effective route was intravenous, but the intramuscular route was satisfactory. He gave at least 350 mg per kilogram of body weight. (A 70 kg man is 150 pounds; thus 70 x 350= 24,500 mg. He would use a 25 gram dose for a 25 gram illness.) This amount was put in 500 cc of sterile water, usually with dextrose, saline or Ringer’s solution. It was diluted so that there was at least 18 cc of dilutent to each gram of C. In small children, 2 or 3 grams can be given intramuscularly once every two hours. An ice cap to the buttocks will prevent soreness and induration. As much as 12 grams can be given in this manner into 2 or 3 different muscle sites with a 50 cc syringe; larger amounts must be diluted with dextrose or saline and run in by I.V. drip. If big concentrated doses are given by push (25 grams in a 100 cc syringe), the brain may become dehydrated causing convulsive movements of the legs. Intramuscular injections are always 500 mg to 1 cc solution. At least one gram of calcium gluconate must be added to the fluids each day. Massive doses of C pull calcium ions from platelets; and the clotting mechanism is weakened. Nosebleeds may occur. One gram of calcium gluconate is added to control acidity and to replace the calcium ion loss
“Sodium ascorbate is less painful. Some of us will put procaine, 2%, with the Vitamin C when injected into the muscle. Vitamin C can also be taken orally once the patient is recovering.
“This oral dose is repeated every hour for 6 to 12 times and then every 2-4 hours until recovery.
“If using under 400 mg per kg body weight, it can be given with the sodium salt. Doses over 400 mg per kg of body weight must be diluted to at least one gram to 18 cc of solution.
“He suggests the following for each bottle: 60 grams of C, 500 mg thiamin HCl, 300 mg pyridoxine, 400 mg calcium pantothenate, 100 mg riboflavin, 300 mg niacinamide. It is to be given once or twice daily.
“He used a 23 gauge needle intravenously and a 22 gauge needle for intramuscular use—one inch long for children and one and a half inch for adults.
“The idea of these big doses is to saturate the tissues; the white blood cells will be able to destroy pathogens. “I have seen diphtheria, hemolytic streptococcus infections clear within hours following an injection of ascorbic acid in a dose ranging from 500-700 mg per kilogram of body weight given intravenously as fast as the patient’s cardiovascular system will allow.”
LHS—“Klenner’s Comments: AA utilization by the body
in malignancy.
“The part very large doses of ascorbic acid given intravenously over a prolonged period offers a medical challenge.
“From cabbage and tomatoes grown in the carbon-14 chambers radioactive ascorbic acid can be extracted, which can be used in tracer studies. At least one research team has demonstrated that in cancer all available "C" is mobilized at the site of the malignancy. Lauber and Rosenfeld reported that "C" is mobilized from the tissues of the body and selectively concentrated in traumatized areas.
“In one hopeless case we administered 17 grams daily for 92 consecutive days without changing the blood or urine levels from that associated with scurvy.
“This is the reason we believe a dose range of 100 grams to 300 grams daily by continuous intravenous drip for a period of several months might prove surprisingly profitable. Blood chemistry should be followed daily with such an investigation. Schlegel found that even a dose of 1.5 grams a day, by mouth, would prevent bladder cancer.” [Italics- added]
LHS—“Klenner’s Cancer Protocol
His protocol for treating
cancer is printed here in total, although I do not understand the rationale for
some of the ingredients. All of this is designed to kill the cancer cells by
shoring up the immune system. He even recognized the therapeutic value for a
positive attitude.
Use radioactive cobalt when and where indicated. [Also Surgery]
Give 45 grams of sodium ascorbate intravenously every twelve
hours for one month. Then use 60 to 65 grams in 500 cc of normal saline or 5%
dextrose in water for five days a week until a cure is obtained. It usually
takes five months. [Comment:
This dosage is, perhaps, too low. The concentration-time math needs to be
calculated]
LHS—“Details: Klenner Protocol
·
Each
bottle is to contain one gram of calcium gluconate, a cc of some B complex,
plus 1,200 mg of thiamin, 300 mg of pyridoxine, and 600 mg of niacinamide.
·
Oral sodium ascorbate, 5, 10, 20, grams daily. The dose depends upon
the bowel tolerance. [Especially
between IV s; split dose to 6-12 times
per day, to reduce depletion to low blood levels]
·
Vitamin
A palmitate, 50,000 units, daily, orally.
·
Pantothenic
acid, (B5) one gram orally four times a day.
·
Amino
acid protein powder with all the eighteen amino acids. 60 tablets each day or,
if a powder, several tablespoons daily. This supports the immune system and the
enzymes.
·
Tyrosine
should be taken separately, if possible, as this one makes the others [Aminos]
work better; 500 mg tablets—six daily.
·
In
addition, a high protein diet using white chicken meat, fresh fish, chicken
livers, and brown-shelled eggs. Beef (but once a week) should be as lean as
possible: lean stew beef or sirloin tip are the best but have the butcher grind
it three times. Hamburgers? Only once a week. Fruit and fruit juices are
permitted. [Not the sugar fortified artificial drinks] Almonds are excellent.
·
No sugar and no starches. UofWashington: Ely: Glycemic
Modulation of Tumor Tolerance [Very important see Ely’s paper, quoted
below]
·
30
to 40 apricot almonds should be chewed every day in divided doses until a
continuous bitter almond taste develops. At this point the patient cuts the
dose in half. “This will form cyanide by way of the stomach acid. Cyanide will
kill cancer cells. Vitamin C will protect one against the lethal effects of
cyanide. It is the antidote.
·
500
mg tablets of vitamin B17 are available. One after each meal and at bed time.”
(Not everyone would agree with this part of the therapy. Cancer victims are
still getting amygdalin B17, as injections from Mexico, but there is some doubt
as to its efficacy. LHS)
·
Vitamin
E, d-alpha tocopheryl acetate, 400 International unit size, 3,200 units daily.
Don’t take iron with it.
·
One
pint of grape juice daily.
·
B
complex tablets with 100 mg of each of the B’s and 100 mcg of B12. Six to eight
tablets daily.
·
Theragran-M
or a similar capsule with all the minerals to replace what is being pulled out
by the C.
·
Maintain
the hemoglobin at 13 grams.
·
Keep
a good attitude.
LHS--“Dr Klenner summarized this paper with this:
“The results suggest that
larger daily amounts could be given in a hospital with faster results. I would
suggest at least 100 grams in 1000 cc of fluid and given every twelve to 24
hours.
[Comment: Problem with long
delays between IVs, the AA depletes to negligible in a few [3-4] hours without
oral supplementation]
“The vitamins and the
calcium gluconate also must be given.” He thought interferon could be assayed
while the patient is in the hospital. “How long will it take for the general
population to challenge the drug cartel?”
LHS--“Klenner’s tests during treatment:
He noted a monitoring
method: “In all virus infections the Benedict urine reaction for sugar will run
from two to four plus. After Vitamin C, this positive reaction will clear in 18
to 36 hours.” [indicating no
antioxidant AA in the urine]
We all know that Vitamin C
is related to glucose and Vitamin C in the urine will show a reducing reaction,
just as glucose does. If a healthy individual is given one or two grams of C by
injection, the urine will show a positive Benedict sugar reaction for hours.”
This paradox, Dr. Klenner
explains, indicates that Vitamin C and the virus bodies do form a new compound,
and not a reducing chemical, otherwise with all this Vitamin C injected, there
would be an increase in the response to the Benedict test.
When the urine starts to
show a positive test to Benedict’s test, it is a sign that the virus is under
control and the person is close to normal again. The Benedict’s urine test is a
guide to treatment with C.
More than 30 years ago, Dr.
Klenner developed the silver nitrate urine test. When treating severe
pathological conditions, the test done every four hours will reveal the level
of Vitamin C saturation. If the urine test is positive for Vitamin C, it means
the tissues are saturated and the patient is on the right dose. It is not a
waste; some spillage indicates saturation.
Note: AA reducing
(antioxidant) form turns silver nitrate 2-4% solution black. If the color
change is not observed, no antioxidant AA is in the urine, therefore the
patient’s AA needs are undersupplied.
LHS--“From Klenner’s Case Histories:
Vitamin C will control
myelocytic leukemia with 25-30 grams orally daily.
Small basal cell epithelioma:
30% Vitamin C ointment.
He cites a disturbing study:
particles resembling viruses were found in some breast milk samples of women
with breast cancer. Could this help to explain why some cancers seem to be
“inherited?” It makes sense that all members of cancer prone families should be
taking at least ten grams of C daily.
He reported a case of a man
with [swollen] lymph glands all over his body. He got the above treatment and
although the glands increased in size for a while, his liver and spleen were
back to normal size in four months. Dr. Klenner noticed a ‘parachute-like’
substance in the urine. Microscopic examination revealed they were clumps of
cancer cells.
Another case was that of a
woman who had an adenocarcinoma of two years duration. She had had
chemotherapy, two surgeries and extensive radiation over her chest, especially
the neck area where the cancerous glands were. The cancer had spread to her
lungs, her abdomen and six glands in her neck. Dr. Klenner gave her the above
protocol. In three months the lesion in her lung had cleared and gone were the
glands in her neck. After six months of intravenous Vitamin C and the B
complex, the abdominal masses had disappeared, but she could not swallow food.
The radiation had scarred her esophagus beyond dilatation and she refused more
surgery. The cancer was gone; she died from starvation due to the radiation.”
End LHS—Quotations
Too much sugar, diabetes,
increases tumor tolerance of the immune system.
UofWashington:
Ely: Glycemic Modulation of Tumor Tolerance
“Among the most striking effects in medicine are
glycemic modulation of tumor tolerance and the associated improvements in
health of cancer patients that can occur within months in the well nourished
but semi-fasting state. We cite evidence that strongly supports the old
view (Good 1970) that neoplastic initiations are always occurring but, in the
cancer-free population, are found and reversed by immune surveillance performed
by leukocytes, as part of Cell Mediated Immunity (CMI). Part of that
evidence shows the 30, 100 and 10,000 fold increases in cancer incidence that
result when immune surveillance is diminished by hyperglycemia or lost
(as by thymectomy, etc). In essence, although not as drastic as thymectomy of
course, hyperglycemia suppresses and hypoglycemia enhances immune
surveillance (in the conditioned patient whose
hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis does not produce a lympholytic state by
excessive elevation of cortisol). Our use of "leukocytes" includes
three major nucleated cells of the blood: granulocytes (or neutrophils),
lymphocytes, and monocytes. The last two are effectors of CMI.”
From Linus Pauling Institute (LPI) at Oregon State University:
LPI Quotes:
LPI: “Studies in the 1970s and 1980s
conducted by Linus Pauling, Ewan Cameron, and colleagues suggested that “very
large doses” of vitamin C [Sodium Ascorbate] (10 grams/day intravenously for
ten days followed by at least 10 grams/day orally indefinitely) were helpful in
increasing the survival time and improving the quality of life of terminal
cancer patients.
Note: Ten
days of IV each day for ?? hours each day.
Most current clinical practice IV SA is not every day and not on
weekends. The cure concentrations were not achieved by the cited Mayo Clinic
studies, a greater concentration is called for. Even these IV concentrations
and durations are considered low today based on years of clinical practice.
Comment: Today in 2011, this dosage appears to be quite low, see Cathcart’s vitamin C levels, below. The blood AA half lifetime is ½ hour. Advanced stage cancer also depletes antioxidant AA, additionally, even more.
LPI: “However, two randomized
placebo-controlled studies conducted at the Mayo Clinic found no differences in
outcome between terminal cancer patients receiving 10 grams/day of vitamin C orally
or placebo. There were significant methodological differences between the Mayo
Clinic and Pauling's studies, and recently, researchers from the NIH suggested
that the route of administration (intravenous versus oral) may have been the
key to the discrepant results.
Comment:
This is true, and is the reason the Mayo trial failed. The AA dosage was still much too low in the
blood. The depletion pharmacokenetics
are shown in a table below. Also see:
Dr Robert
Cathcart: Preparing Vitamin C solution
for IV/Injection use
Cathcart:
Vitamin C Levels/Frequency vs. Disease/Condition
LPI: “Intravenous (IV) administration can
result in much higher blood levels of vitamin C than oral administration, and vitamin
C levels that are toxic to cancer cells in culture can be achieved in humans
only with intravenous but not oral administration of vitamin C.
Comment: However in
treatment, high levels of oral AA must be taken every few hours during the days
between IV AA administration and also during the days of administration.
LPI: “Dr. Mark Levine and colleagues at NIH have
investigated the anticancer mechanism responsible for vitamin C and reported
that it involves production of hydrogen peroxide, [inside the cancer cell]
which is selectively toxic to cancer cells.
Comment: Selectively toxic means that the depleted
form of AA is not toxic to normal cells.
This is because cancer cells have a higher metabolic use of oxygen and
are oxygen starved. Thus the oxidizing
form of AA (DHA) is disruptive to the cells energy pathways.
Comment: Vitamin C has two forms: Anti-Oxidant and
Oxidizing (depleted) form. The Oxidizing form is active against cancer cells.
The Oxidizing form is Dihydro
Ascorbic Acid (DHA).
LPI: “Thus, it appears reasonable to reevaluate the
use of high-dose vitamin C as adjunctive cancer therapy.
LPI: “Currently, there are
no results from controlled clinical trials indicating that vitamin C would
adversely affect the survival of cancer patients.”
[Because National Cancer
Institute repeatedly turned down proposals]
See: Linus Pauling: The [In-]Effectiveness of the National Cancer Institute [1977, After $-billions, Still no AA studies, Why?]
Degression from LPI
to present successful clinical results:
No “controlled clinical trials” is not the same as “No successful clinical results”.
The site doctoryourself.com (Author Andrew W Saul, PhD) has material documenting high dosage Sodium Ascorbate IV treatments. His books are highly recommended.
Review of Andrew Sauls cancer
book: I HAVE CANCER: WHAT SHOULD I DO? Book
Finder at AddAll
Riordan Team’s IV AA
Protocol PDF, contains the figures.
See: Description of Riordan’s IV methods: Intravenous Ascorbate as a Chemotherapeutic and Biologic Response Modifying Agent (Summary without Figures) by The Center for the Improvement of Human Functioning, International, Inc., Bio-Communications Research Institute. A discussion of successful application of AA IV to treating various cancer conditions that matches the criteria below.
Necessary Treatment Dosage Criteria:
The proper design of a treatment trial should include providing tested (not assumed) blood AA levels that are high enough concentrations to exceed the killing concentrations for cancer cells in vitro. Papers exist with these cell kill blood AA concentration levels published for various cancer cell lines. The duration of the AA levels at killing concentration must include several hours each day of maintenance of the killing concentration. Between the IVs high level AA oral intake is also needed. High levels of glucose blocks AA utilization and high oxide levels consumes AA instantly.
Considering that the AA blood half-life is ½ hour. A two hour delay between AA administration implies a depletion to 1/16 the initial level. An eight hour delay in intake means the level depletes to near zero. In the presence of a systemic disease condition, with accompanying toxins and reactive oxides ROS/NOS, the AA is much more rapidly oxidized than given in the table below. Rapid AA metabolization depletes stored reserves and requires replacement at intervals like it is a food, not a catalytic agent. This shows why frequently repeated and never missed oral AA supplementation is needed with pathologies.
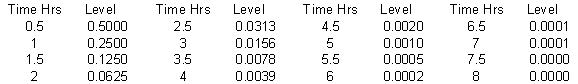
Back to LPI material LPI Clinical Trials
LPI: “Recently, two phase I clinical trials in
patients with advanced cancer found that intravenous administration of vitamin
C at doses up to 1.5 g/kg of body weight was well tolerated and safe in
pre-screened patients; other phase I trials are ongoing. Additionally, phase II
clinical trials evaluating the efficacy of vitamin C in cancer treatment are
currently under way.
LPI: “Some case reports have suggested that
intravenous vitamin C may aid in cancer treatment. However, vitamin C should
not be used in place of therapy that has been demonstrated effective in the
treatment of a particular type of cancer, for example, chemotherapy or
radiation therapy.”
Note: Proper IV SA success statistics may be much greater than conventional treatments. Both can be used together, but some oncologists do not want to permit IV SA, and will abandon the patient who seeks supplemental treatment. Get another oncologist. Others report AA is protective for normal cells damaged by radiation and chemotherapy, and it potentates these therapies in killing cancer cells.
LPI: “If an individual with cancer chooses to take
vitamin supplements, it is important that the clinician coordinating his or her
treatment is aware of the type and dose of each supplement. While research is
under way to determine whether combinations of antioxidant vitamins might
be beneficial as an adjunct to conventional cancer therapy, definitive
conclusions are not yet possible.”
Note the “combinations of
antioxidant vitamins” this
indicates a major misunderstanding of how IV SA works. SA operates against cancer cells as an
oxidant, not as an antioxidant.
Comment: There is a dispute that if AA permits
better tolerance of radiation or chemotherapy by permitting normal cells to
recover more quickly, that this will also help to protect the cancer cells. Since AA in high concentrations is not toxic
to normal cells but is toxic to cancer cells, acting as an oxidant. It does not appear that AA will interfere
with the conventional therapies; instead it should enhance them.
LPI: “For more information about intravenous vitamin
C and cancer, see the Linus
Pauling Institute Spring/Summer 2006 Research Newsletter.
LPI: “In a presentation at a meeting of the American
Cancer Society, a scientist suggested that supplemental vitamin C might enhance
the growth of cancer cells or protect them from cell-killing free radicals
produced by radiation and some forms of chemotherapy. An article published in
the Spring/Summer 2000
issue of the Linus Pauling Institute Newsletter, Is vitamin C harmful
for cancer patients?, provides additional insight on this topic.
LPI: “For information about the clinical use of
high-dose intravenous vitamin C as an adjunct in cancer treatment, visit the University
of Kansas Medical Center Program in Integrative Medicine Web site.
End LPI material.
Matthias Rath, was a Pauling associate:
Quote: “Cancer tumor growth can be stopped” http://www.drrathresearch.org/cancer.html
Matthias Rath claims cancer halted with vitamin C +
lysine + proline + green tea extract
“We have developed a specific synergistic combination of nutrients that can inhibit invasion of cancer cells in the tissue and control other key mechanisms of cancer at the same time. This synergy utilizes a nutrient mixture (NM) of vitamin C, the amino acids lysine, proline, arginine, N acetylcysteine, green tea extract (EGCG) as well as copper, manganese and selenium”.
Using both in vitro and in vivo approaches, we provided comprehensive scientific data that this nutrient synergy can:
Inhibit tumor growth and cancer
metastasis:
The following relevant mechanisms have been affected by this nutrient synergy
· Inhibition of secretion and expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) curtailing connective tissue digestion
· Inhibition of cancer cells invasion in the tissue (confirmed in almost 40 types of cancer cells)
· Optimizing composition of connective tissue towards increasing its integrity and resistance to degradation
· Decreased cell multiplication resulting in the inhibition of tumor growth.
As a result we demonstrated in vivo that the spread (metastasis) of cancer cells can be largely inhibited by the administration of nutrient synergy in the diet or by iv and ip delivery.
Ketosis helps; Glycemia hinders effective treatment See AA
Ketonic Protocols
Serrapeptase
Enzyme (SpE) Attacks Tumor Sheath helping to
dissolve and reduce the tumor.
Case Histories of serrapeptase enzyme have shown significant tumor and cyst reduction starting immediately. Read our Serrapeptase Case Histories. Serrapeptase is sold in the U.S. as a nutritional supplement. Dosage is about 120000 units at taken at 2-3 x per day on totally empty stomach with 2-3 hours before and after each ingestion. Higher dosages of SpE are reported safe. Latent lung neoplasm reduction can produce blood in sputum. Serrapeptase and some infections results in strong Herx reactions for fibromyalgia thought to be Lyme disease related. Many long-term (years) users report it holds off recurrence of calcium nodule formation and pain in arthritis.
Rome Cancer Clinic treats Cancer as
a Fungal/Yeast (Candida)
Infection using Sodium
Bicarbonate
Dr. Tullio Simoncini is a roman doctor specializing in oncology, diabetes and in metabolic dysfunctions. His studies of the polymorphisms of the many fungal forms of Candida albicans are largely ignored or attacked by less knowledgeable clinical practitioners. See His Clinic Website This an example where biology knowledge is extensive but the knowledge has failed to be appreciated by the medical profession. The pub med shows the sodium bicarbonate PH control is effective to limit the spread of some cancers and is ineffective for some others, like melanoma. Browse his website and see for yourself.
Gerson’s Diet that cures cancer:
See:
Gerson's Diet that cures
cancer Movie Gerson's Speech
bibliography of
published clinical studies showing Gerson treatments' benefits
bibliography
of all of Dr. Gerson’s scientific writings.
FDA
Ban on pre-formulated AA injections
The reason given is that the shelf life of AA
solutions is very short. It needs to be
mixed a few hours before administration.
Otherwise the amount of AA delivered is not guaranteed to have the
intended strength or effectiveness.
This is an entirely legitimate concern.
The emotional hype from Natural News, below, is a
distortion of the facts, but it is typical of the public reactions, where the
government tries to limit the access to a healing modality known to work. Increasing the access to inexpensive healing
modalities is preferred by the public, but is often lobbied against by the
profit making medical and drug interests to restrict competition.
“False: FDA Moves to Ban Injectable Vitamin C, Further Destroying the Health of Americans”
Quote: Source: Natural News http://www.anh-usa.org/action-alert…
“Counterpoint provided at
bottom – the FDA is NOT banning IV Vitamin C.
“Several websites, this one included, took the original report for face value and failed to investigate the claim further. …. Regardless, it has placed the subject of IV C onto a lot of people’s radar who might have otherwise never heard of it or the awesome benefits of ascorbic acid in the fight against cancer.
“Not content to kill 100,000
Americans each year with deadly Big Pharma drugs while censoring the truth
about the healing effects of herbs, nutritional supplements and natural
medicines, the FDA has now set out to deny
Americans access to yet another lifesaving medicine known simply as vitamin C.
“As reported by the Alliance for Natural Health, the FDA has notified a manufacturer of injectable vitamin C that it will be criminally prosecuted if it continues to manufacture this lifesaving nutritional therapy.”
Comment: Following the new rules AA
administration will be more dependable.
The FDA action may have resulted in the suspension or invalidating of cancer trials of “megadose” IV/C. These trials may have to be restarted/redesigned, a delay in publication, and a boon for the cancer industry.
Physicians will be required to obtain their vitamin C solutions for injection, freshly made, and in small quantities from compounding pharmacies, or make it themselves.
Physicians doing a high volume of IV/C may wish to adopt Dr. Cathcart's method of preparation. We predict that physicians using Cathcart-style IVs will observe significantly increased positive responses if their SA solutions are fresh and of known composition.
From Wikipedia:
AA/SA Antioxidant/Oxidant mechanisms:
Ascorbic acid is a mild reducing agent. For this reason, it degrades upon exposure to oxygen, especially in the presence of metal ions and light. (or in the presence of oxides in the body) It can be oxidized by one electron to a radical state or doubly oxidized to the stable oxidizing form called dehydroascorbic acid.
|
Top: ascorbic acid of Vitamin C) |
|
Bottom: dehydroascorbic acid of Vitamin C) |
Ascorbate reduced form usually acts as an antioxidant. It typically reacts instantly with oxidants of the reactive oxygen species, such as the hydroxyl radical formed from hydrogen peroxide. Such radicals are damaging to animals and plants at the molecular level due to their possible interaction with nucleic acids, proteins, and lipids. Sometimes these radicals initiate chain reactions. Ascorbate can terminate these chain radical reactions by electron transfer. This protects cells from oxide free radicals.
Ascorbic acid is special because it can transfer a single electron, owing to the stability of its own radical ion called "semidehydroascorbate".
Ascorbate oxidizing form Dehydroascorbate. The net reaction is:
RO• + C6H7O6−→ ROH + C6H6O6−•.
The oxidized forms of ascorbate are relatively unreactive, and do not cause cellular damage to normal cells.
However, being a good electron donor, excess
[Dehydro] ascorbate in the presence of free metal ions can not only promote but
also initiate free radical reactions, thus making it a potentially dangerous
pro-oxidative compound in certain metabolic contexts. In the absence of O2
.
Outside the cancer cells, the body needs a lot of antioxidant AA. The AA blood levels deplete to a critical level and then histamine is released. Then NO and hydrogen peroxide levels rise exponentially. The blood levels near death are severely depleted of the antioxidant AA. Administering a lot of AA to the terminal cancer patient neutralizes the NO and peroxides. This eases greatly the discomfort. For the seriously ill, the administered AA converts rapidly to the depleted, oxidizing, dehydroascorbate form.
Then this oxidizing form of AA easily passes into the cancer cells. It takes the place of sugar in the same pipelines that feed cells. Infected cells and cancer cells have a strong need for sugar. Inside the oxygen starved cancer cell dehydroascorbate acts to produce hydrogen peroxide to kill the cell. This mechanism also works to kill other (epithelial and blood/immune) cells invaded by viruses or bacteria.
Book: Vitamin C, Infectious Diseases, and Toxins: Curing the Incurable, by Thomas E. Levy, M.D., J.D. http://www.tomlevymd.com
We asked Dr. Levy for his advice on recommending specific IV/C dosages. This was his kind response:
“Dosage is always empirical, as in give more if the clinical response, especially in infections or poisonings, is not adequate. “One gram per kilogram of body weight would be a very good general guide, which would be about 20 to 25 grams for a 50-pound child and 100 grams for a 220 pound-adult. However, just giving most adults 50 grams at a time for most conditions works out well. Rate of infusion can range anywhere from 30 minutes to 3 hours, depending upon comfort of the IV, the amount being administered, and the condition being treated. (toxins, more rapid, infections, cancer, etc., less rapid). The more rapid infusions will often be associated with hypoglycemia, which can usually be easily addressed with a little fruit juice or even a candy bar. But it is best if the added glucose/sugar can be avoided. 50, 75, or 100 grams of stock solution can each go in 500 cc sterile water. I would always go with 100 grams for most cancer patients, as long as it was well tolerated. “Since you can give the stock solution IV push, there should be no arbitrary limit to how much you can add. However, it's a bit difficult volume-wise to put much more than 100 grams in a 500 cc bottle, unless you take significant water out. And remember, this is for pure sodium ascorbate infusions. Many other vitamins and minerals need much more attention to detail with regard to concentration. Really, unless you are treating a very small toddler or infant, you should be giving 25, 50, 75, or 100 grams of sodium ascorbate in a bottle. Otherwise, giving IV C based on 1 gram per kilogram of body weight should be specific enough.“Powder is better than vitamin C crystals when making lots of solution. I do think the Millipore filtration is important, and the magnetic stirrer is very important when doing this on a regular basis.”
References: Most relevant Vitamin C tribal knowledge
Historical Vitamin C Ascorbate
Articles 1930s to 1990s
Irwin
Stone: The Healing Factor: Vitamin C Against Disease, 1972
Oregonstate.edu:
Linus Pauling Institute Vitamin C
Different
Forms of Vitamin C, Linus Pauling Institute's Micronutrient Information Center
Sweden
Lund Univ: Dehydroascorbic acid clears Alzheimer plaques in mice
Klenner and Cathcart References
Orthomed.com
Robert Cathcart Preparing Vitamin C solution for IV/Injection use
Dr
Robert Cathcart: Medical Tribune Letter: Clinical Trial of Vitamin C (1975)
Dr.
Robert Cathcart: Medical Tribune Letter Vitamin C Function in AIDS (1983)
AA vs. Viral Diseases List
and References
John Ely References on Nutrition, AA, CoQ10, and Life Extension
UofWashington: Ely: Ascorbic Acid and Some Other Modern Analogs of the Germ Theory, 1999
UofWashington: Ely: On Population Kinetics of an Aging Society: Aging and Scurvy
UofWashington: Ely: Glycemic Modulation of Tumor Tolerance Sugars feed Cancer
UofWashington: Ely: On the Science of Essential Nutrients 2002 “Unprofitable Modalities”
UofWashington: Ely: Hyperglycemia Epidemic B6 and Nutrition
UofWashington: Ely CoQ10 Summary of Ref Abstracts Physicians Update on CoQ10
UofWashington: Ely & Krone: "Brief Update Ubiquinone = CoQ10"
UofWashington: Ely & Krone: "Urgent Update Ubiquinone = CoQ10" Turnover and daily consumption
UofWashington: Ely Langsjoen "Intro to CoQ10"
Other Important References
L. Pauling: Lysine/Ascorbate-Related Amelioration of Angina (Arterial Sclerosis) [JOM 1991]
Theodore Jorgensen Physicist Letter November 2003
Johns Hopkins: Vitamin C & E cut ICU deaths by 50%
Reduced Risk of Alzheimer Disease in Users of Antioxidant Vitamin Supplements
Aloe vera gel increases bioavailability ~3x of vitamins C & E
Fonorow: CO-Q10, Statins, Vitamin C 2003 Bolenreport.com Headlines:
Harvard: Vitamin C only 1 of 880 substances to regenerate heart muscle from stem cells
Harvard study of 85,000 (15-Years) finds single vitamin C pill [daily] reduces heart disease almost 30%
Risk of stroke was 70% higher in the bottom quartile than in the top quartile for serum vitamin C
Vitamin C inhibits lipid oxidation in human HDL
More vitamin C as pills reduce cataracts by 77%
Carnitine, its building blocks vitamin C and lysine, increase muscle strength
Matthias Rath claims cancer halted with vitamin C/lysine/proline and green tea extract
Vitamin C boosts immune system in as little as 5 hours (NIH)
Vitamin C pills extend life 6-years (USC)
Vitamin C (and lysine) halt atherosclerosis
IV vitamin C reverses endothelial dysfunction
Vitamin C - new treatment for osteoporosis
Vitamin C can (1) prevent aortic deterioration; and (2) cure large aortic aneurysms without surgery.
Vitamin C dissolves cholesterol gallstones
Vitamin C dissolves Alzheimer’s plaques assists in brain cell regrowth.
High-dose vitamin C completely prevented drug-induced amnesia in mice
Vitamin C vs. Hyaluronate Lyase Enzyme
Bacterial agents restore antibiotic action
Cetyl Myristoleate natural compound valuable in arthritis conditions
DETERMINATION OF VITAMIN C FINAL PRACTICAL (200 POINT) EXERCISE Updated 04-13-03
Streptococcus pneumoniae hyaluronate lyase: Overview
GlycoForum-GlycoScience-Science of Hyaluronan
Herpes Viruses And Associated Diseases
Microbiology - Bio. 321 - Fall semester 2003 - 4th quarter lecture notes
Hub for Integrated Medicine Diabetes II VitaC
Nutrition Vitamin C - Wikibooks, collection of open-content textbooks
transhumanism « Human Enhancement and Biopolitics